
BIO SYNBIOTICS
DOWNLOAD PDF
CONTACT US
INFORMATION
TODAY
- biosynbiotic1drink.pdf


DOWNLOAD PDF
CONTACT US
INFORMATION
TODAY

sales@biosynbiotics.com

(Nutritional Regiment, Exercise Program, Detox Program
and
Digestive enzymes/Probiotic Supplement Program)
Facts
An article in USA – 14 August 2012
US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Research Date
More than one-third of U.S. adults (35.7%) are obese.
Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Children overweight stands at 37% Obesity now affects 17% of all children and adolescents in the United States

Why is this happening?
Many foods today are refined to the extent that they don’t have any nutrients anymore, compared to the foods of the past which would have healthy nutrients that our body could absorb.
Many of us today have convenience all around. An example of this is compared to my years ago where people had to walk or cycle distances to get around, many of us today have cars that we utilize for even short distances. An accumulation of these conveniences lead to less energy exerted leading to a buildup of fats.
To further understand the situation we have to look at the factors: Why, How, Risks Involved and The Solution.
Why do we become overweight?
1. Genetic Factor
Genetics may account for up to 50 percent to 70 percent of your weight variability, meaning those with poor genes may have a harder time losing weight.
It is far more likely that genetics influences your lifestyle and food choices, not your weight itself. While genes may mean you have a harder time controlling cravings, or feeling full, this doesn't mean weight loss is impossible -- you simply have to work harder to stay motivated, regulate your calorie intake and move more.
2. Bad eating habits
Depending Some habits people have that can contribute to weight gain: they eat most of their meal out, always eat more than necessary (more carbohydrates than proteins), take in too much sugars, skipping meals, not drinking enough water.
3. Emotional factor
Studies have linked anxiety, depression and anger with overeating for many people, and researchers at Leeds University found that when people feel very stressed they tend to eat high fat, high sugar snacks rather than healthier main meals and vegetables.
4. Hormonal imbalance
Your hormones control every aspect of weight loss including your metabolism, where you store your fat, your appetite and even your cravings. This means any form of hormonal imbalance will hinder your efforts – regardless of your diet and exercise habits.
5. Metabolic disorder
Approximately one in every 10,000 people will have adult onset growth hormone deficiency. People with adult growth hormone deficiency have an increased risk of heart disease and strokes as a result of the physical changes that occur in body fat, cholesterol and circulation. Healthy living, a balanced diet and exercise to prevent becoming overweight are essential to reduce this risk.
Certain prescription drugs used to treat mood disorders, seizures, migraines, diabetes, and even high blood pressure can cause weight gain.
We all know how our feeling and environment have a effect on our diets which in turn affects our waistline.
Classification of Overweight and Obesity by BMI, Waist Circumference and Associated Disease Risks
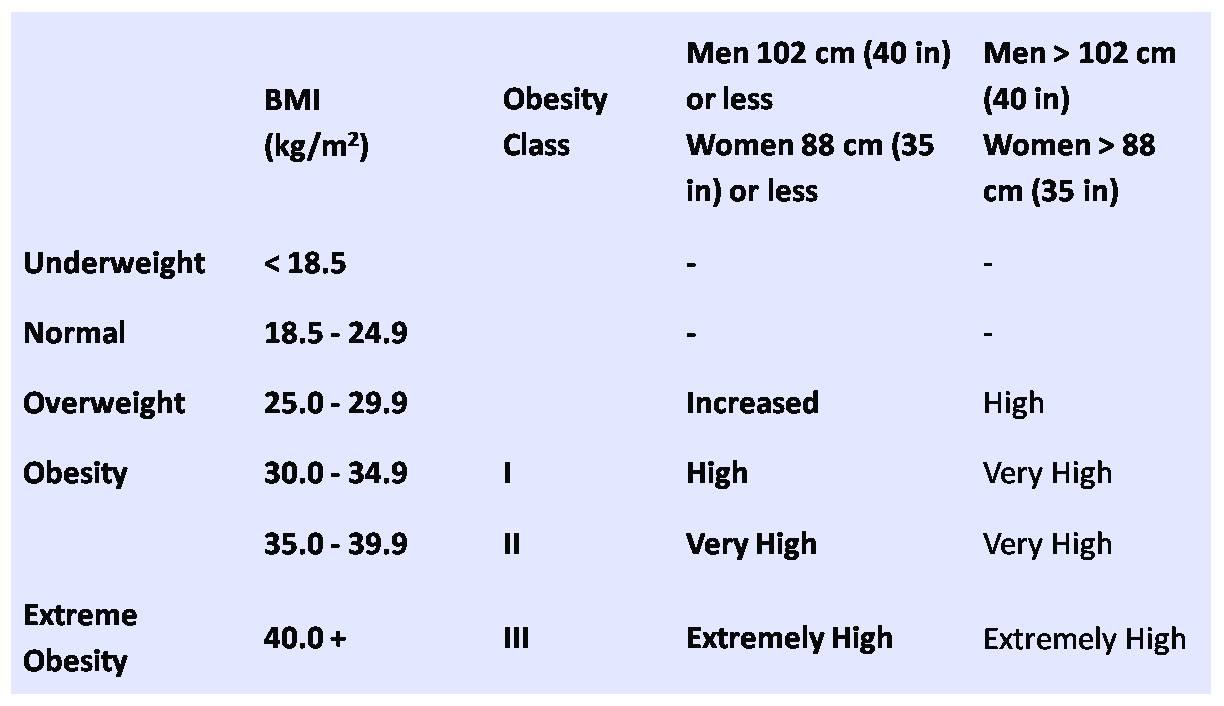
* Disease risk for type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and CVD.
+ Increased waist circumference can also be a marker for increased
risk even in persons of normal weight. SOURCE: National Heart, Lung
and Blood Institute 2010
It is known that weight is tied into healthy living but it is also important to note that weight is also proportionally tied to rate of aging, in essence the more the body has to cope with added weight the faster we age.
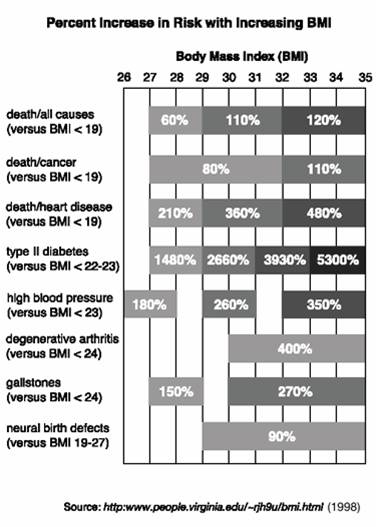
As we can see from the chart above the higher up in BMI we go, meaning the more weight in proportion to our height, the risks of certain problem double and eventually triple, compared to that of lower BMI percentages.
Our weight directly greatly affects our health risks!
Key Measurements of Overweight &
Obesity
How do we define Overweight & Obesity?
BMI classification
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple index of weight-for-height that is commonly used to classify underweight, overweight and obesity in adults.
|
BMI = |
Weight (kg) |
|
Height x Height (in meters) |
Example:
Male
Weight - 70 kilograms
Height - 1.75 meters
|
BMI = |
70 |
|
1.75 x 1.75 |
|
BMI = |
22.85 |
The normal range for males is between BMI 18.50-24.99, our example fall under that category.
BMI calculation is just a guideline to follow as it gives a general weight range to aim for if weight loss is your goal. In the next few pages we will look at the increased risks depending on your current BMI.
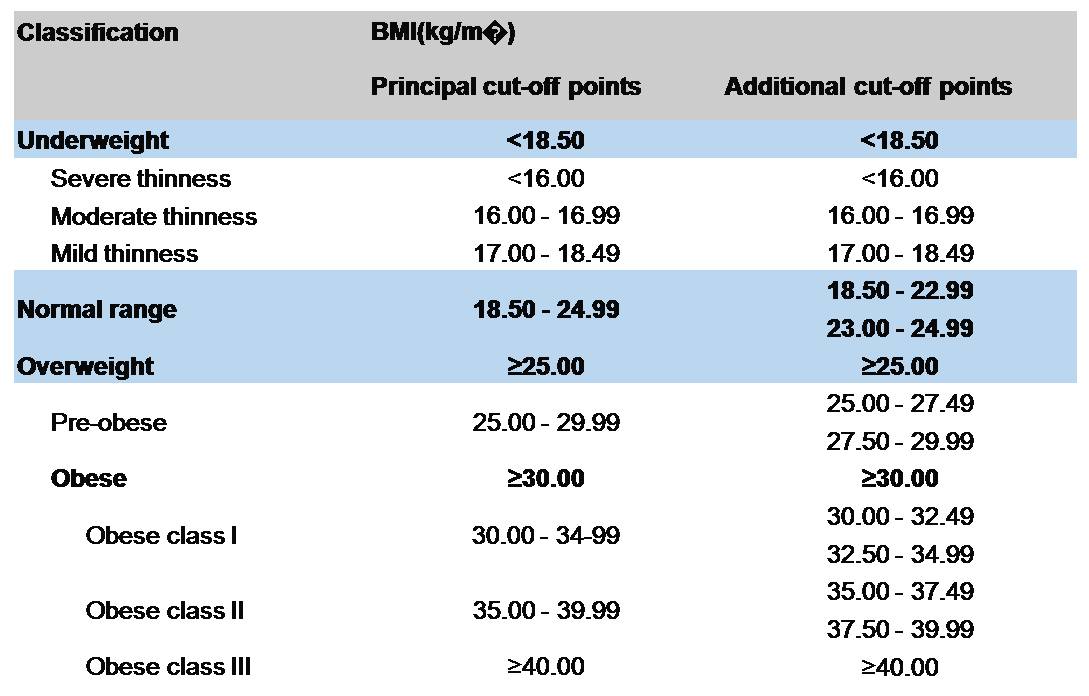
The International Classification of adult underweight, overweight and obesity according to BMI

2014 Copyright . All Rights Reserved
contact us at enquiry@biosynbiotics.com